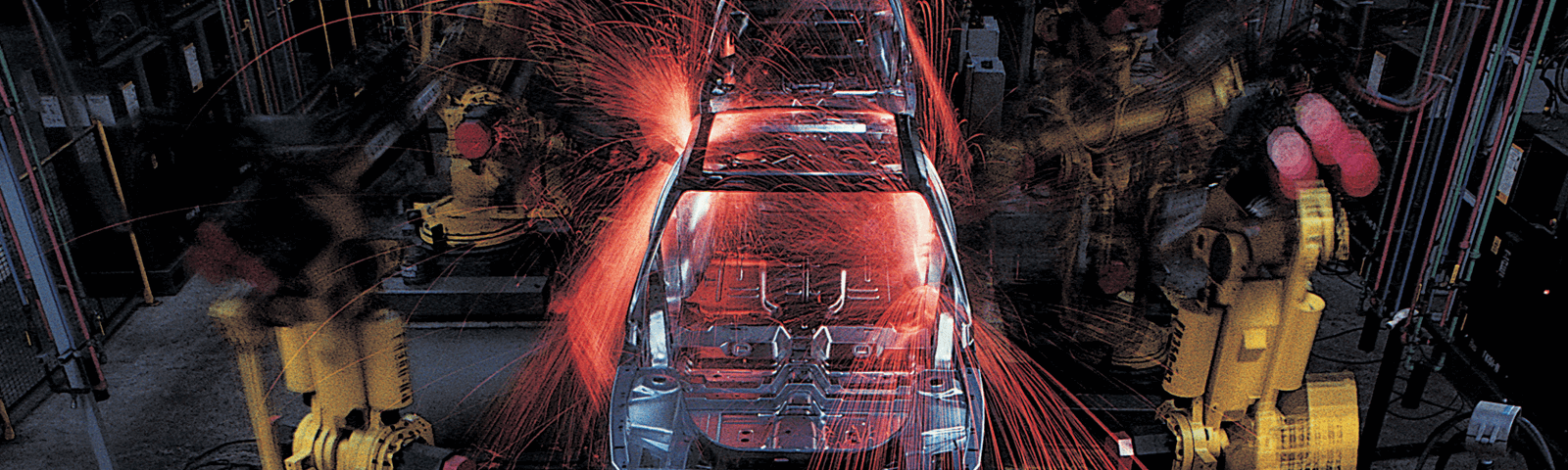
Automotive Manufacturers seek seamless production processes to meet increasing and changing demand patterns. Reaching higher levels of productivity and profitability for these companies goes hand-in-hand with the need for continuous improvement and optimization of production systems and equipment. By planning towards system optimization and operational efficiency, you can manage expenses and investments to secure competitive advantage.
Read Brochure
Digital Trends Shaping the Automotive Industry
How is technology disrupting the automotive market? Below are three trends that are seen to impact the industry:
Big Data Integration
- Automotive manufacturing is leading digital innovation by integrating big data and technology in all levels of the manufacturing process, from design to execution, to simplify workflow and make it more efficient.
- Core to digitalization is the volume of big data collected. Data gathered from automotive design conceptualization up to aftermarket services opens new avenue for manufacturers to understand customer buying behavior; identify inefficiencies in systems/processes; ultimately accelerate sales.
- Data collected from miles driven by vehicles will be used to influence safety, aerodynamics, performance, power algorithms and other fundamental elements of the vehicle design.
- To enhance efficiency and flexibility of assembly lines, data gathered throughout the car building process will be used in predictive analysis to improve manufacturing simulations and monitor machine performance.
Increasing Electronics and Software Content
- Electronic systems continue to contribute more than 90 percent of innovations and new features to car models, with focus on quality and safety, and infotainment for product differentiation
- Forging closer customer relationship and increase margins with installation of telematics features, including semi-autonomous driving aids such as automatic parallel parking, lane-keeping assistance, and sensor-based reporting on car maintenance and usage
- The increase usage and importance of infotainment and telematics systems puts pressure on industry players to install state-of-the-art information technology systems and software to ensure proper deployment, testing, and maintenance of these systems
Energy Efficiency in Automotive Manufacturing
- Through the years, automotive manufacturers have explored and developed next generation materials in vehicle design that highly improved the energy efficiency of production processes and equipment. These new materials and equipment use less energy which constitute to lower carbon emissions in their manufacturing facilities and equivalent cost savings
- Energy is lost during the manufacturing process due to production inefficiencies and technological limitations. These energy losses can include waste heat escaping in gases or liquids, energy embodied in rejected parts that must be reprocessed, losses from transmission or delivery of energy from one part of the plant to another, or energy represented in fluids that are wasted or must be disposed of. Automotive manufacturers are seeking to lessen and eradicate these energy losses by redesigning processes, upgrading systems, and finding new ways to reuse waste energy
Infrastructure Challenges
- Growing customer demands and expectations are putting pressure on manufacturers to make sure they meet or even exceed production schedules.
- Protection of manufacturing equipment is critical, as downtime means lost productivity, penalties, damaged reputation and lost revenues.
- There are many causes of downtime, but many equipment-related failures can be preventable.
- Therefore, it is important to maintain reliability through regular facility testing and by utilizing solutions that protect against common causes of breakdowns such as power surges and electrical spikes.

- With increased reliance on automation and artificial intelligence, manufacturers must be able to come up with ways to seamlessly integrate technology into everyday manufacturing operations.
- AI and robotics are increasingly being used on the manufacturing floor to speed up manufacturing processes.
- Manufacturing equipment should be optimized and designed to accommodate technology integration through the use of predictive tools as well as power availability.

- Digitization and automation are increasingly being adopted by manufacturers to improve efficiency and overall operations.
- Manufacturers must be able to come up with ways to seamlessly integrate technology into everyday manufacturing operations.
- Equipment should be optimized and designed to accommodate technology integration through the use of predictive tools as well as power availability.
- IT infrastructure becomes all the more critical in the age of automation and IoT, and IT managers must have the right infrastructure in place not only to support the uptick in compute requirements, but also to manage the entire manufacturing facility better and smarter.
- The use of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML) & Robotics in manufacturing means an uptick in computing power and demand. Necessary solutions that are rugged and efficient are critical to support corporate demands in a manufacturing environment.
- As they strive to create a leaner, more efficient supply chain systems, manufacturers need to be aware of key supply and demand information in real time, right up to the shop floor – to be able to adjust production SKUs and schedules.
- A facility or IT manager will need to be able to see a problem before it becomes a problem – and be able to do something about it.
- Predictive monitoring tools can aid in having a smarter supply chain network. These tools must be able to predict, diagnose and provide action on all areas of the manufacturing network (from the environment, equipment or IT network) to ensure process continuity at all times.

Vertiv Protects Critical Processes in the Automotive Space
| Sub-Assembly | Assembly and Post-Assembly |
| Inbound Parts Distribution and Storage | Information Technology |
| Facilities and Laboratories |
Featured Vertiv Solutions
Liebert ITA2
Compact, Efficient, & Robust UPS for Critical Applications
Liebert Hipulse-U
Utmost Reliable Power Solution for Critical Business Applications

SmartCabinet™
Intelligent, Integrated Containment for IT Infrastructure
Liebert® DM
High Performance Cooling for Small Technological Rooms

